Shearer's inequality
In probability theory, Shearer's inequality states that if X1, ..., Xd are random variables and S1, ..., Sn are subsets of {1, 2, ..., d} such that every integer between 1 and d lies in exactly r of these subsets, then
where 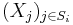 is the Cartesian product of random variables
is the Cartesian product of random variables 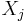 with indices j in
with indices j in 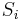 (so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of
(so the dimension of this vector is equal to the size of 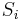 ).
).
![H[(X_1,\dots,X_d)] \leq \frac{1}{r}\sum_{i=1}^n H[(X_j)_{j\in S_i}]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/5a21678d6766571ea248495f77b755fc.png)